Bamboo
Learn how to integrate Atlassian Bamboo CI with Golive with particular focus on:
Video Tutorial
Relationships between Bamboo and Golive concepts
Bamboo concept | Detail | Golive equivalence | Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
Project | Group logically build plan together. | - | - |
Build Plan | Define the build process of your software and usually result in output binaries named artefacts | - | - |
Artefacts | Output result of a build, usually a "physical" binary (jar, zip, war...) of your application that can be added to a release for being deployed on an environment | - | - |
Stage | Represents a specific step in your build plan. It's composed of jobs that can be run in parallel. Plan can be composed of several stages and you can trigger different action on its successful execution (eg: deployment, trigger another plan...). A stage could be used to group the different jobs used to compile your software, and another stage could be used to group all the testing jobs. | - | - |
Job | A job contains the sorted list of tasks (shell scripts, ant, maven, command) used to build your software. | - | - |
Task | An atomic operation. Could be a shell script, an ant or maven command, a git operation... | Tasks are used to publish data from Bamboo to Golive using the Rest API that can be called by a script task (eg: curl) | |
Release | Releases are used to track exactly what software was deployed to an environment. In essence, a release is a snapshot of any number of artifacts that will be used in the deployment process. Releases are versionned and they follow a naming convention that can be used by Bamboo to automatically generate the next available version number when the full chain is fully automated. | Deployment | In Golive, current version of a specific application on a specific environment is tracked by a Deployment object. Golive provides a Rest API that can be called to create a new deployment and update the deployed version of an environment. By synchronising Bamboo releases with Golive deployments, your Jira users will be able to always get the current up to date deployment information + all history of past deployments. |
Deployment Project | Deployment project is the container that holds:
| - | In some ways, you can see Bamboo deployment projects and projects as something that can be easily mapped with Golive application concept, more details below. |
Environment | An environment is the mapping of a deployed release on a specific subset of machines. Environment contains its deployment plan (similar to build plan but to deploy a release on a specific machine/environment) which defines how a specific release (a set of artefacts) will be published on its environment (that can be composed of several machines). It's in this deployment plan that we are going to add additional steps to publish/synchronise the release version between Bamboo and Golive | Environment (Application-Category) | Golive Environment is the equivalent of Bamboo Environment. It's defined by the combination of an Application (eg: eCommerce) and a Category (eg: Prod, QA, Demo...). An environment can have one status and one release number deployed at a time. In Bamboo, even if an environment is described as "Staging", it may be composed by several applications. In Golive you may split this environment into several environments per application (ex: eCommerce Staging and ERP Staging) if you want to easily differentiate their technical requirements, lifecycle,... That's why in Golive environments are defined by the combination of a category (eg: Staging, Prod...) and an application (eg: eCommerce, ERP...). You can naturally freely decide how you want to model and map environments in both tools. |
Application | Golive provides to Jira the concept of Application, that you can use to map your applications to your Jira projects and Jira versions. |
Continuous Integration Use Case
In our use case, you will learn how to automatically push deployment information to Golive when a deployment is triggered in Bamboo.
To achieve this, you have to add one task to your existing build process. This task will publish new release version to Golive using the Rest API.
Screen flow
In Bamboo, we can see how project and environment have been structured:
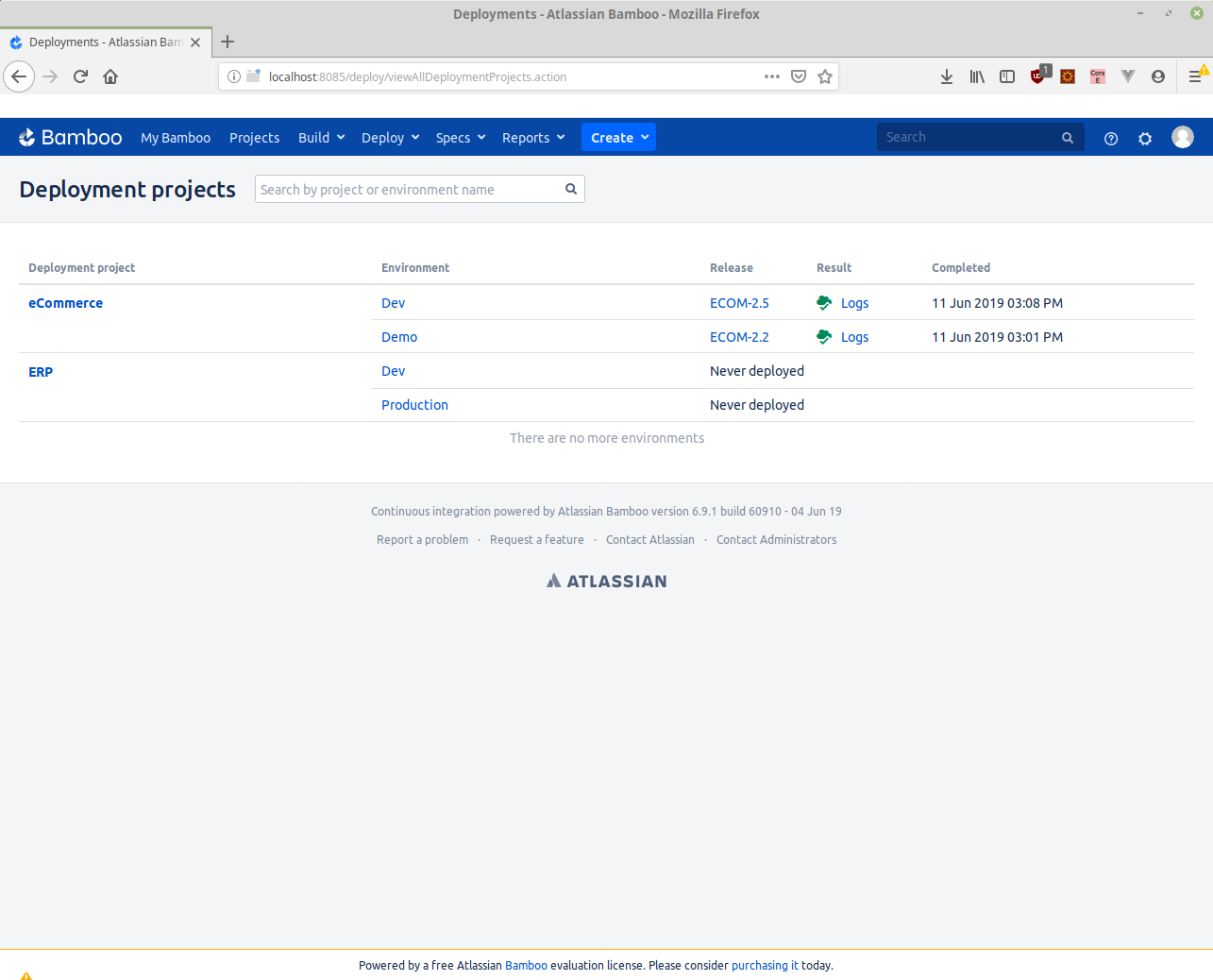
Here the equivalent environment structure in Golive:
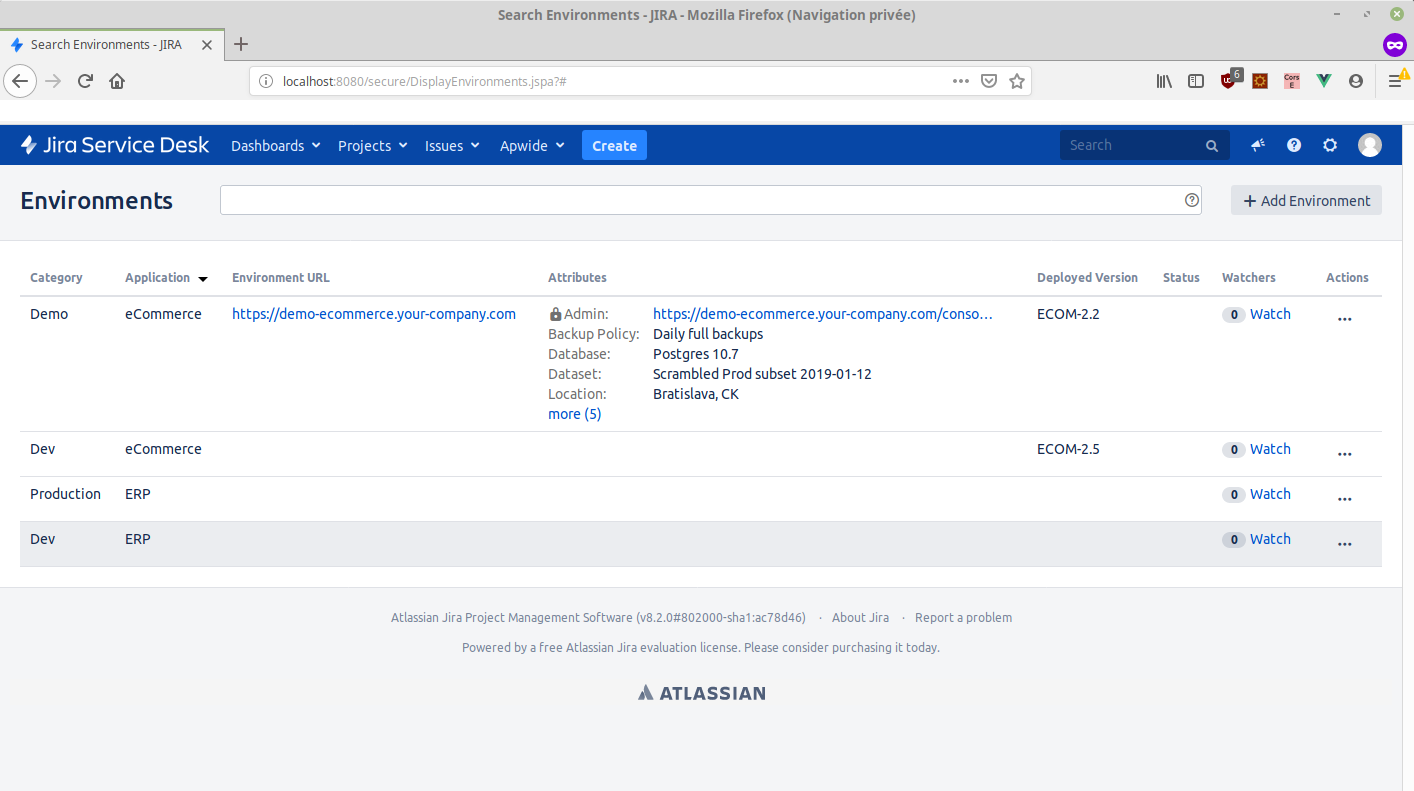
Now, if we look at the deployment plan in bamboo for the dev environment, we can see the following tasks:
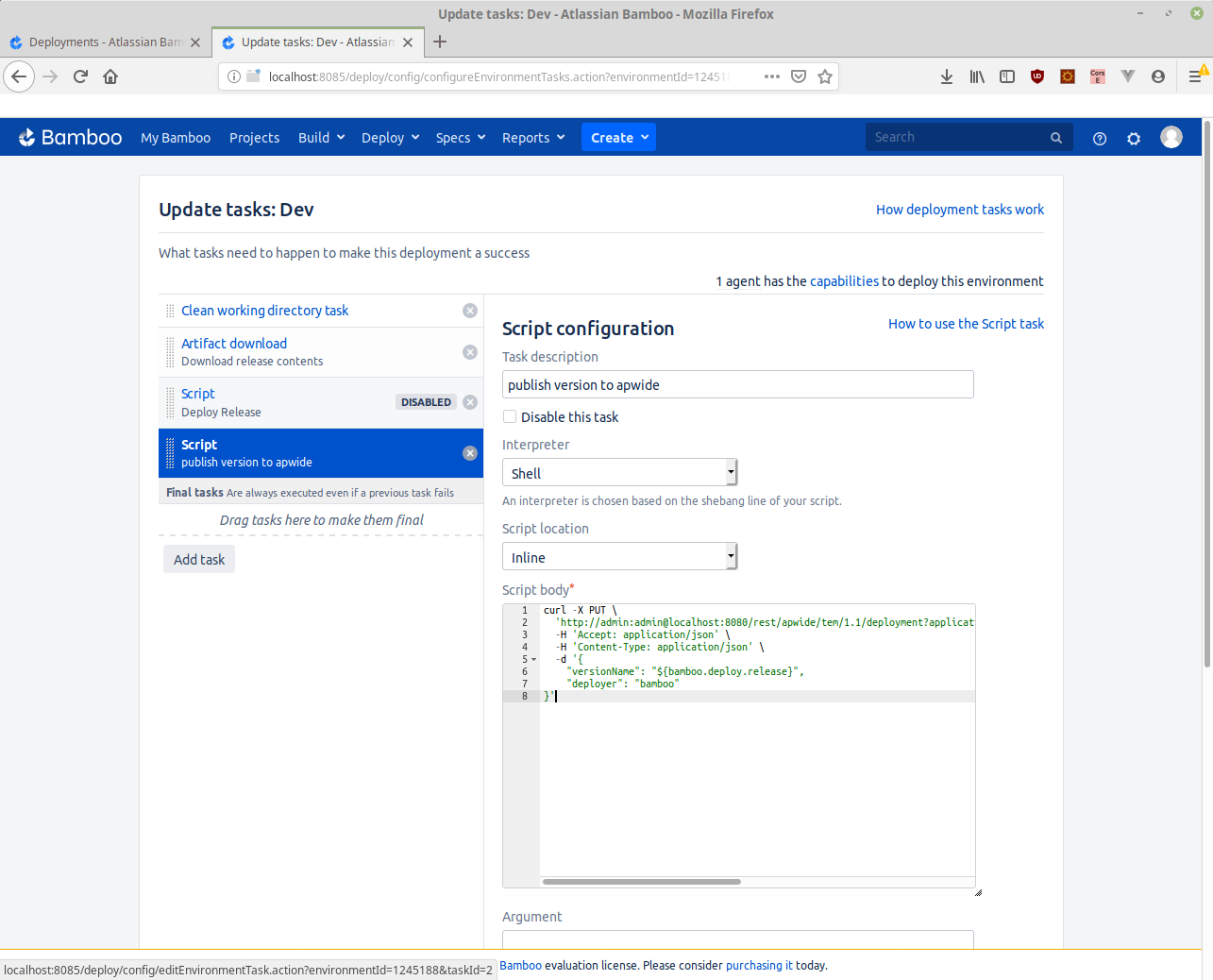
We have added a curl script to call the Golive Rest API
Script samples to call Golive Rest API from Bamboo:
Update status to "deploy"
curl --user ${bamboo.apwide.user}:${bamboo.apwide.password} -X PUT \
'${bamboo.apwide.url}/status-change?application=${bamboo.deploy.project}&category=${bamboo.deploy.environment}' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Deploy"
}'Update deployed version
curl --user admin:admin -X PUT \
'http://localhost:8080/rest/apwide/tem/1.1/deployment?application=${bamboo.deploy.project}&category=${bamboo.deploy.environment}' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"versionName": "${bamboo.deploy.release}",
"deployer": "bamboo"
}'Update environment attributes
curl --user ${bamboo.apwide.user}:${bamboo.apwide.password} -X PUT \
'${bamboo.apwide.url}/environment/${bamboo.apwide.environment.id}' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"url": "${bamboo.application.url}",
"attributes": {
"Last Deploy Result URL": "${bamboo.resultsUrl}",
"Bamboo Environment URL": "${bamboo.bamboo.url}/deploy/viewEnvironment.action?id=1245188",
"Bamboo Application URL": "${bamboo.bamboo.url}/deploy/viewDeploymentProjectEnvironments.action?id=1146883",
"Owner": "${bamboo.environment.owner}",
"Database": "${bamboo.environment.database}",
"OS": "${bamboo.environment.OS}",
"# servers": "${bamboo.environment.servers}"
}
}'Update status back to "up"
curl --user ${bamboo.apwide.user}:${bamboo.apwide.password} -X PUT \
'${bamboo.apwide.url}/status-change?application=${bamboo.deploy.project}&category=${bamboo.deploy.environment}' \
-H 'Accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "Up"
}'Bamboo variables
You can use variables from:
or create your own custom global variables:
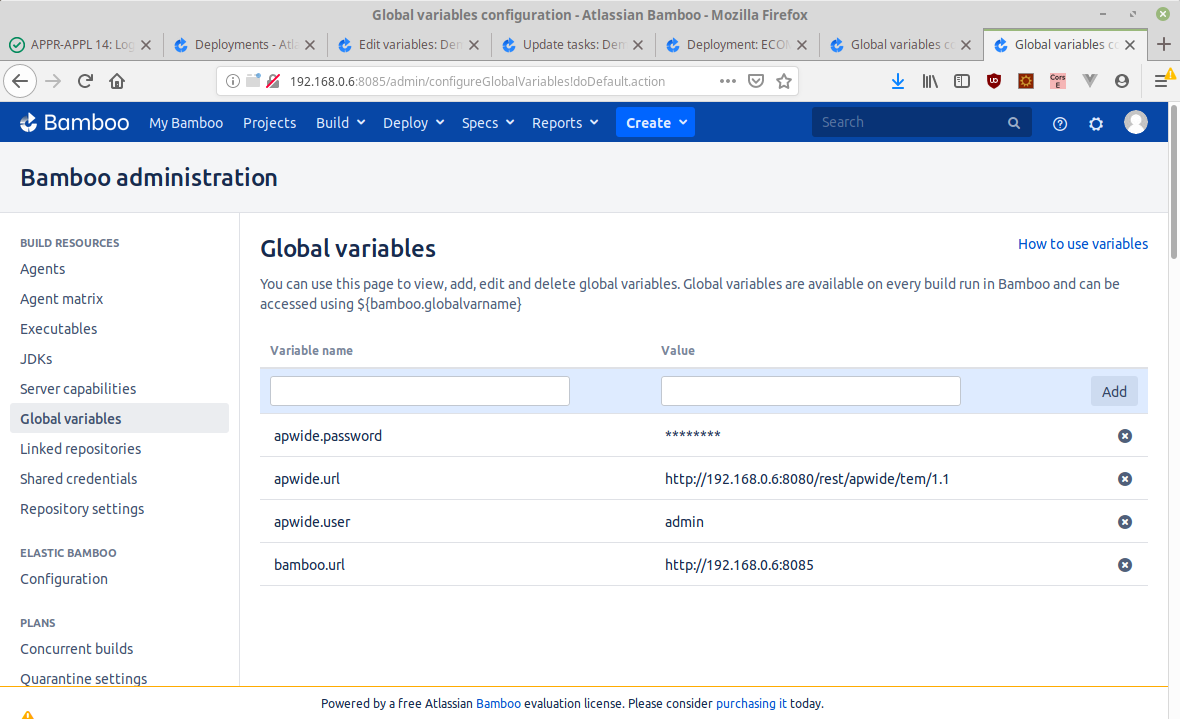
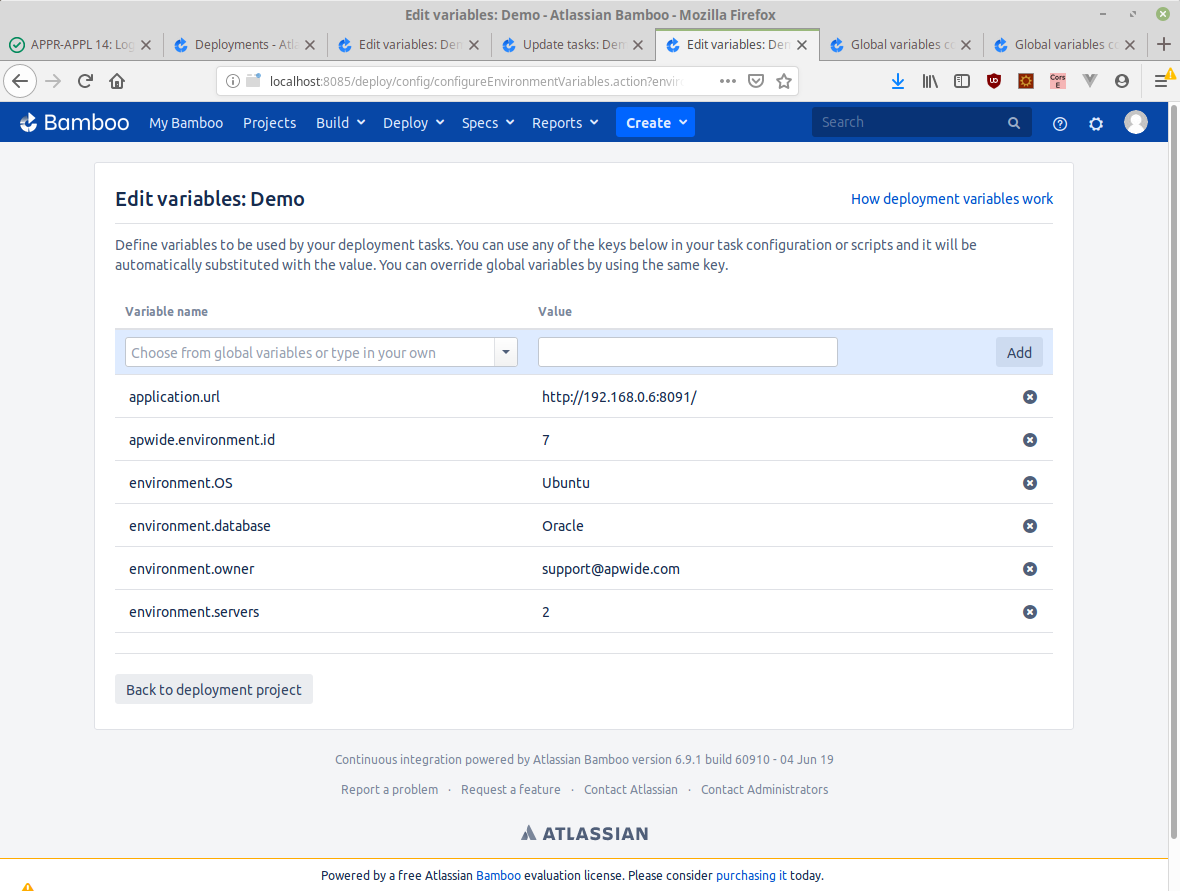
or even create some environment specific variables:
Build and Deployment Process Example
A commit is triggered on an SCM
Build plan, located in a specific project (eg: eCommerce) is triggered
When build is successful, artefact is generated and made available to other build/deploy plans
In a deployment project (eg: eCommerce), a trigger is configured to trigger deployment to an environment (eg: Dev) when the corresponding project build plan was successfully built
A release (following the naming convention scheme) is generated containing the artefacts
The deployment plan deploy the release to the environment
The last task of the deployment plan updates de the deployed version of the corresponding environment in Golive
Recommendations
In Bamboo, if a deployment plan is triggered several times with the same release on the same environment (with the same version number), Golive will not consider this deployment as a new deployment. You should add something different (ex: build number) in the name of the deployed version in order to track this kind of change in Golive deployment history.
If you proceed with the following mapping, you can easily reuse Bamboo variables to complete the call to the Golive Rest API :
Bamboo deployment project to a Golive application
Environment name to Category Name
Release name to deploy version name
Golive Rest API credentials should never be declared in clear in the tasks (use global variables).
